Where Forex Brokers Really Earn: A Closer Look at Their Income Sources

💼 Where Do Forex Brokers Make Their Money? Here’s the Real Deal
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “How do Forex brokers make money if I’m just trading currency pairs?”, you’re not alone. Many new traders are curious about what happens behind the scenes of a broker’s business model.
The truth is, Forex brokers make money in more ways than you might expect—and not all of them depend on traders losing money.
Let’s dive into the core ways brokers generate revenue and how this impacts your trading experience.
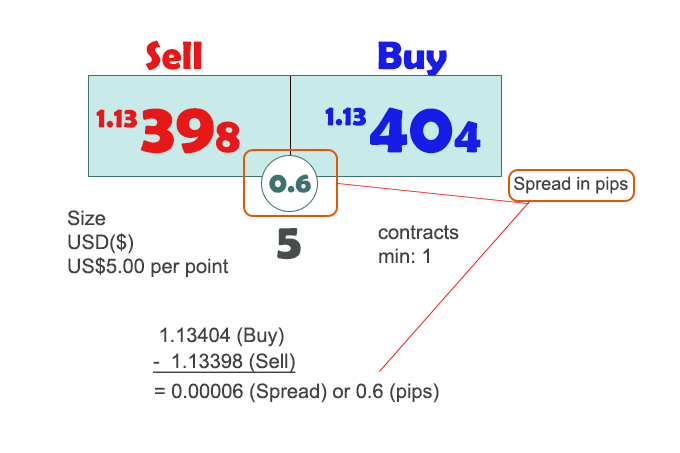
📊 1. Spreads: The Silent Profits in Every Trade
One of the most common ways brokers earn is through spreads—the difference between the buy (ask) and sell (bid) price of a currency pair.
Here’s a quick example:
- USD/JPY Buy Price: 150.02
- USD/JPY Sell Price: 150.00
- Spread = 2 pips
That 2-pip difference may seem small, but across hundreds or thousands of trades, it adds up to real income for the broker.
💰 2. Fixed Commissions on Trades
Some brokers, especially those offering direct market access (DMA) or ECN-style trading, charge a flat commission per trade instead of widening the spread.
This model appeals to traders who want raw, low spreads and clear cost structures. The commission is usually based on trade size and asset type.
🔍 3. Spread Markups by Market Makers
Certain brokers act as market makers, meaning they provide liquidity to traders by quoting prices themselves. They may mark up the actual spread before presenting it to you.
So instead of a raw 1-pip spread from the interbank market, you might see a 2-pip spread—and that extra pip goes to the broker as profit.
🌙 4. Holding Fees (Swaps)
If you leave a position open overnight, you could pay or receive a small fee called a swap. Brokers often pass part of this fee to the liquidity provider and keep a portion for themselves.
Swap rates are influenced by interest rate differences between the currencies you’re trading and are usually visible on the broker’s platform.
📊 5. Revenue from Trading Volume & Client Flow
Some brokers profit from high trading volumes by routing trades to liquidity providers or acting as the counterparty for losing positions.
They might analyze trader behavior and use it to manage risk internally—especially if the broker operates a B-Book model. While this isn’t always unethical, it should be clearly disclosed.
🛠️ 6. Premium Services and Platform Extras
Aside from trading fees, brokers may offer:
- Paid signal services
- Copy trading platforms
- VPS servers for automated strategies
- Subscription-based education or tools
These extras often come at a cost—and while some are worth it, others can be overhyped. Always research what you’re paying for.
⚠️ Be Broker-Savvy: What to Look For
To protect your trading capital, always evaluate:
- Is the broker licensed and regulated by major authorities?
- Do they publish fee structures transparently?
- Are there hidden charges on withdrawals, inactivity, or swaps?
Being informed means you won’t fall for high-cost traps or poor service.
🧭 Final Thoughts
Understanding how brokers make money gives you a huge edge as a trader. You’ll know what to expect, how to manage your costs, and which broker types are aligned with your strategy.
Whether they’re profiting from spreads, commissions, swaps, or add-ons, a reputable broker will be clear about how they earn—and how much you’ll pay.